first of all good morning..afternoon..evening to all of you.
this is the parts you needed to assemble your pc..
1.)
ProcessorCentral processing unit (CPU), the part of a computer that interprets instructions.A silicon chip that contains a CPU. In the world of personal computers, the terms microprocessor and CPU are used interchangeably. At the heart of all personal computers and most workstations sits a microprocessor. Microprocessors also control the logic of almost all digital devices, from clock radios to fuel-injection systems for automobiles.
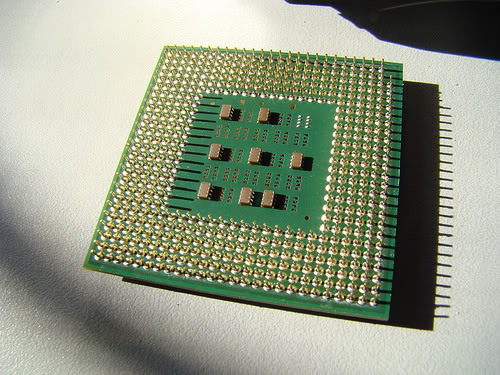
2.)
Video CardA video card, also referred to as a graphics accelerator card, display adapter, graphics card, and numerous other terms, is an item of personal computer hardware whose function is to generate and output images to a display.

3.)
Memory (RAM)RAM (random access memory) is the place in a computer where the operating system, application programs, and data in current use are kept so that they can be quickly reached by the computer's processor. RAM is much faster to read from and write to than the other kinds of storage in a computer, the hard disk, floppy disk, and CD-ROM. However, the data in RAM stays there only as long as your computer is running.

4.)
Mainboard/MotherboardThe main circuit board of a microcomputer. The motherboard contains the connectors for attaching additional boards. Typically, the motherboard contains the CPU, BIOS, memory, mass storage interfaces, serial and parallel ports, expansion slots, and all the controllers required to control standard peripheral devices, such as the display screen, keyboard, and disk drive. Collectively, all these chips that reside on the motherboard are known as the motherboard's chipset.
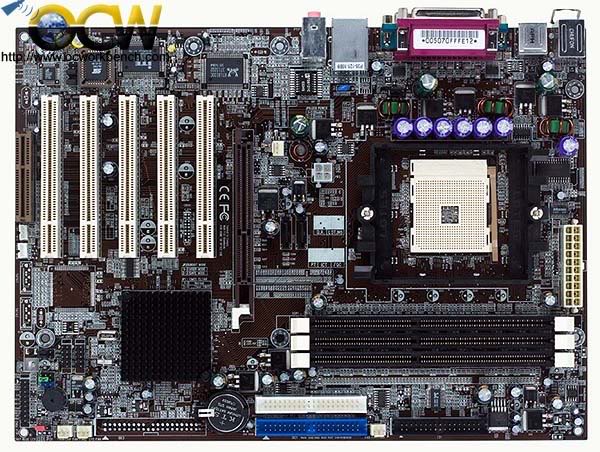

5.)
Power SupplyAlso called a power supply unit or PSU, the component that supplies power to a computer. Most personal computers can be plugged into standard electrical outlets. The power supply then pulls the required amount of electricity and converts the AC current to DC current. It also regulates the voltage to eliminate spikes and surges common in most electrical systems. Not all power supplies, however, do an adequate voltage-regulation job, so a computer is always susceptible to large voltage fluctuations.

6.)
Hard Disk Drive/HDDA magnetic disk on which you can store computer data. The term hard is used to distinguish it from a soft, or floppy, disk. Hard disks hold more data and are faster than floppy disks. A hard disk, for example, can store anywhere from 10 to more than 100 gigabytes, whereas most floppies have a maximum storage capacity of 1.4 megabytes.

7.)
Sound CardAn expansion board that enables a computer to manipulate and output sounds. Sound cards are necessary for nearly all CD-ROMs and have become commonplace on modern personal computers. Sound cards enable the computer to output sound through speakers connected to the board, to record sound input from a microphone connected to the computer, and manipulate sound stored on a disk.
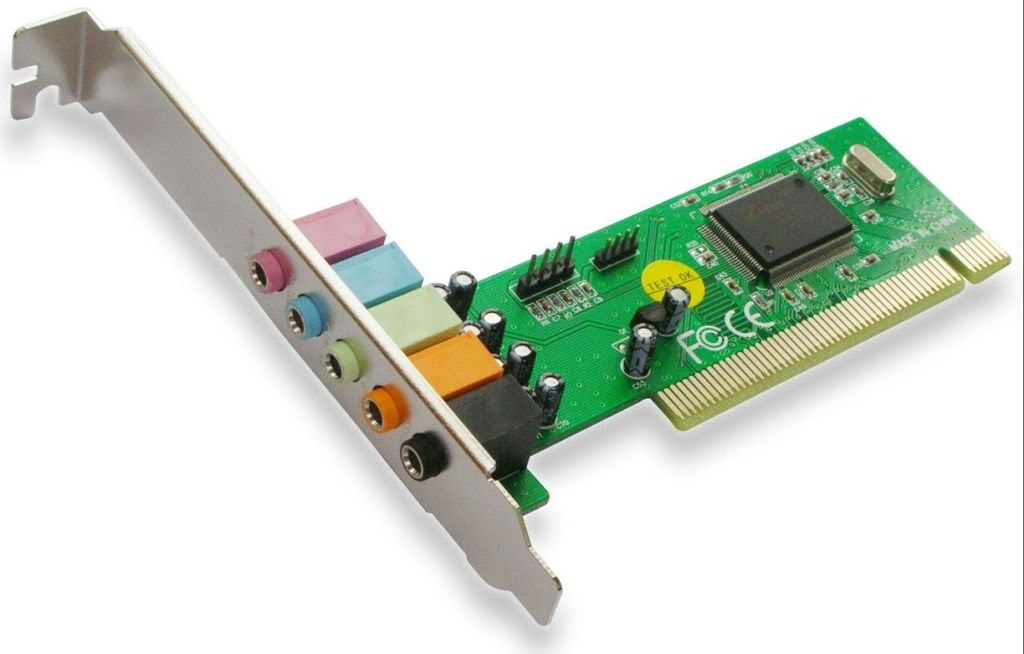

8.)
IDE CableAbbreviation of either Intelligent Drive Electronics or Integrated Drive Electronics, depending on who you ask. An IDE interface is an interface for mass storage devices, in which the controller is integrated into the disk or CD-ROM drive.

9.)
Lan CardA computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected to other LANs over any distance via telephone lines and radio waves. A system of LANs connected in this way is called a wide-area network (WAN).

10.)
CD-RomThe most prevalent types of compact discs are those used by the music industry to store digital recordings and CD-ROMs used to store computer data. Both of these types of compact disc are read-only, which means that once the data has been recorded onto them, they can only be read, or played.

11.)
Computer Casingthis is where you were put that all computer hardwares.

12.)
MouseA device that controls the movement of the cursor or pointer on a display screen. A mouse is a small object you can roll along a hard, flat surface. Its name is derived from its shape, which looks a bit like a mouse, its connecting wire that one can imagine to be the mouse's tail, and the fact that one must make it scurry along a surface. As you move the mouse, the pointer on the display screen moves in the same direction. Mice contain at least one button and sometimes as many as three, which have different functions depending on what program is running. Some newer mice also include a scroll wheel for scrolling through long documents.

13.)
KeyboardThe set of typewriter-like keys that enables you to enter data into a computer. Computer keyboards are similar to electric-typewriter keyboards but contain additional keys. The keys on computer keyboards are often classified as follows:
# alphanumeric keys -- letters and numbers
# punctuation keys -- comma, period, semicolon, and so on.
# special keys -- function keys, control keys, arrow keys, Caps Lock key, and so on.

14.)
MonitorAnother term for display screen. The term monitor, however, usually refers to the entire box, whereas display screen can mean just the screen. In addition, the term monitor often implies graphics capabilities.
There are many ways to classify monitors. The most basic is in terms of color capabilities, which separates monitors into three classes:
# monochrome : Monochrome monitors actually display two colors, one for the background and one for the foreground. The colors can be black and white, green and black, or amber and black.
# gray-scale : A gray-scale monitor is a special type of monochrome monitor capable of displaying different shades of gray.
# color: Color monitors can display anywhere from 16 to over 1 million different colors. Color monitors are sometimes called RGB monitors because they accept three separate signals -- red, green, and blue.


